How to Avoid Fighting Rust Borrow Checker
The 3 important facts in Rust:
- Tree-shaped ownership. In Rust's ownership system, one object can own many children or no chlld, but must be owned by exactly one parent. Ownership relations form a tree. 1
- Mutable borrow exclusiveness. If there exists one mutable borrow for an object, then no other borrow to that object can exist. Mutable borrow is exclusive.
- Borrow is contagious. If you borrow a child, you indirectly borrow the parent (and parent's parent, and so on). Mutably borrowing one wheel of a car makes you borrow the whole car, preventing another wheel from being borrowed. It can be avoided by split borrow which only works within one scope.
Considering reference shape
Firstly consider the reference 2 shape of your in-memory data.
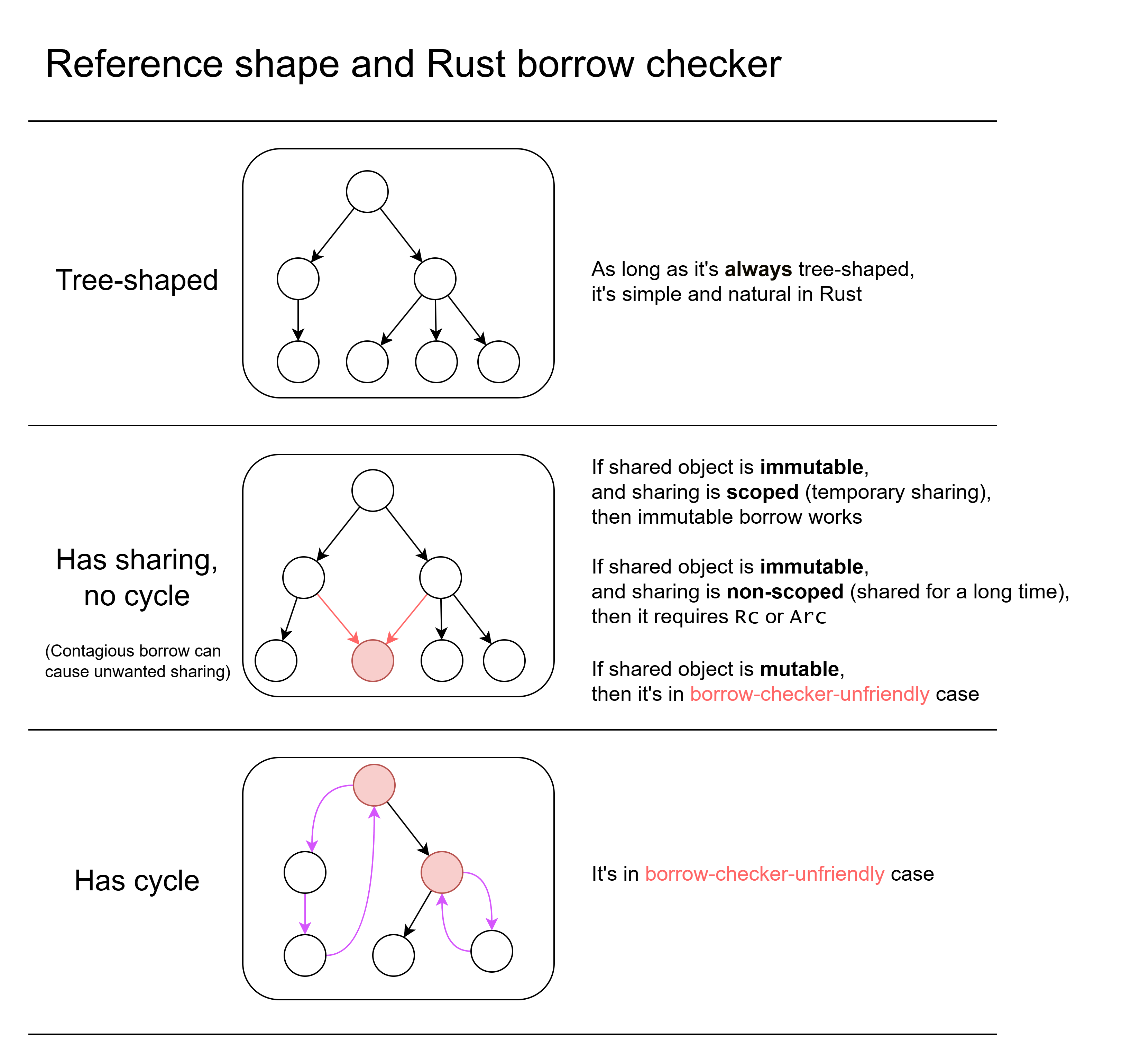
- If the reference is tree-shaped, then it's simple and natural in Rust.
- If the reference shape has sharing, things become a little complicated.
- Sharing means there are two or more references to the same object.
- If shared object is immutable:
- If the sharing is scoped (only temporarily shared), then you can use immutable borrow. You may need lifetime annotation.
- If the sharing is not scoped (may share for a long time, not bounded within a scope), you need to use reference counting (
Rcin singlethreaded case,Arcin possibly-multithreaded case)
- If shared object is mutable, then it's in borrow-check-unfriendly case. Solutions elaborated below.
- Contagious borrow can cause unwanted sharing (elaborated below).
- If the reference shape has cycle, then it's also in borrow-check-unfriendly case. Solutions elaborated below.
The most fighting with borrow checker happens in the borrow-check-unfriendly cases.
Summarize solutions
The solutions in borrow-checker-unfriendly cases (will elaborate below):
- Data-oriented design. (less OOP)
- Avoid unnecessary getter and setter.
- Use ID/handle to replace borrow. Use arena to hold data.
- No need to put one object's all data into one struct. Can seperate to different places.
- Do split borrow in outer scope, and pass related fields separately.
- Defer mutation. Turn mutation as commands and execute later.
- Avoid in-place mutation. Mutate-by-recreate. Use
Arcto share immutable data. Use persistent data structure. - For circular reference:
- For graph data structure, use ID/handle and arena.
- For callbacks, replace capturing with arguments, or use event handling to replace callback.
- Borrow as temporary as possible. For example, replace container for-loop
for x in &vec {}with raw index loop. - Refactor data structure to avoid contagious borrow.
- Reference counting and interior mutability.
Arc<QCell<T>>,Arc<RwLock<T>>, etc. (only use when really necessary) unsafeand raw pointer (only use when really necessary)
Contagious borrow issue
Contagious borrow issue is a very common and important source of frustrations in Rust, especially for beginners.
The previously mentioned two important facts:
- Mutable borrow exclusiveness. If you mutably borrow one object, others cannot borrow it.
- Borrow is contagious. If you borrow a child, you indirectly borrow the parent (and parent's parent, and so on), which contagiously borrow other childs of the same parent. Mutably borrowing one wheel of a car makes you borrow the whole car, including all 4 wheels, then the wheel that you don't use cannot be borrowed. This don't happen under split borrow.
A simple example:
pub struct Parent {
total_score: u32,
children: Vec<Child>
}
pub struct Child {
score: u32
}
impl Parent {
fn get_children(&self) -> &Vec<Child> {
&self.children
}
fn add_score(&mut self, score: u32) {
self.total_score += score;
}
}
fn main() {
let mut parent = Parent{total_score: 0, children: vec![Child{score: 2}]};
for child in parent.get_children() {
parent.add_score(child.score);
}
}
Compile error:
25 | for child in parent.get_children() {
| ---------------------
| |
| immutable borrow occurs here
| immutable borrow later used here
26 | parent.add_score(child.score);
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ mutable borrow occurs here
(That simplified example is just for illustrating contagious borrow issue. The total_score is analogous to a complex state that exists in real applications. Same for subsequent examples. Just summing integers can be done by .sum() or local variable. Simple integer mutable state can be workarounded using Cell.)
That code is totally memory-safe: the .add_score() only touch the total_score field, and .get_children() only touch the children field. They work on separate data, but borrow checker thinks they overlap, because of contagious borrow:
- In
fn get_children(&self) -> &Vec<Child> { &self.children }, although the method body just borrowschildrenfield, the return value indirectly borrows the wholeself, not just one field. - In
fn add_score(&mut self, score: u32) { self.total_score += score; }, the function body only mutably borrowedtotal_scorefield, but the argument&mut selfborrows the wholeParent, not just one field. - Inside the loop, one immutable borrow to the whole
Parentand one mutable borrow to the wholeParentoverlaps in lifetime.
You just want to borrow one field, but forced to borrow the whole object.
What if I just inline get_children and add_score? Then it compiles fine:
pub struct Parent {
total_score: u32,
children: Vec<Child>
}
pub struct Child {
score: u32
}
fn main() {
let mut parent = Parent{total_score: 0, children: vec![Child{score: 2}]};
for child in &parent.children {
let score = child.score;
parent.total_score += score;
}
}
Why that compiles? Because it does a split borrow: the compiler sees borrowing of individual fields in one function (main()), and don't do contagious borrow.
The deeper cause is that:
-
Borrow checker works locally: when seeing a function call, it only checks function signature, instead of checking code inside the function.
The borrow checker works locally because:
- If it checks method body, it need to do whole-program analysis. It's complex and slow.
- It improves decoupling. You don't need to worry a library's changing of function body makes your code stop compling. That decoupling is also required by dynamic linking.
-
Information is lost in function signature: the borrowing information becomes coarse-grained and is simplified in function signature. The type system does not allow expressing borrowing only one field, and can only express borrowing the whole object.
There are propsed solutions: view type. It encodes field-level borrow information into type 3.
Summarize solutions (workarounds) of contagious borrow issue (elaborated below):
- Remove unnecessary getters and setters.
- Just simply make fields public (or in-crate public). This enables split borrow in outer code. If you want encapsulation, use ID/handle to replace borrow of mutable data (elaborated below).
- The getter that returns cloned/copied value is fine.
- If data is immutable, getter is also fine.
- Reorganize code and data structure. 4
- Defer mutation
- Avoid in-place mutation
- Do a split borrow on the outer scope. Or just get rid of struct, pass fields as separate arguments. (This is inconvenient. Unfortunately, borrowing is unfriendly to composition.)
- Manually manage index (or key) in container for-loop. Borrow as temporary as possible.
- Just clone the data (can be shallow-clone).
- Use interior mutability (cells and locks).
Defer mutation. Mutation-as-data
Another solution is to treat mutation as data. To mutate something, append a mutation command into command queue. Then execute the mutation commands at once. (Note that command should not indirectly borrow base data.)
- In the process of creating new commands, it only do immutable borrow to base data, and only one mutable borrow to the command queue at a time.
- When executing the commands, it only do one mutable borrow to base data, and one borrow to command queue at a time.
What if I need the latest state before executing the commands in queue? Then inspect both the command queue and base data to get latest state (LSM tree does similar things). You can often avoid needing to getting latest state during processing, by separating it into multiple stages.
The previous code rewritten using deferred mutation:
pub struct Parent {
total_score: u32,
children: Vec<Child>
}
pub struct Child {
score: u32
}
pub enum Command {
AddTotalScore(u32),
// can add more kinds of commands
}
impl Parent {
fn get_children(&self) -> &Vec<Child> {
&self.children
}
fn add_score(&mut self, score: u32) {
self.total_score += score;
}
}
fn main() {
let mut parent = Parent{total_score: 0, children: vec![Child{score: 2}]};
let mut commands: Vec<Command> = Vec::new();
for child in parent.get_children() {
commands.push(Command::AddTotalScore(child.score));
}
for command in commands {
match command {
Command::AddTotalScore(num) => {
parent.add_score(num);
}
};
}
}
Deferred mutation is not "just a workaround for borrow checker". Treating mutation as data also has other benefits:
- The mutation can be serialized, and sent via network or saved to disk.
- The mutation can be inspected for debugging and logging.
- You can post-process the command list, such as sorting, filtering.
- Easier parallelism. The process of generating mutation command does not mutate the base data, so it can be parallelized. If data is sharded, the execution of mutation commands can be dispatched to shards executing in parallel.
Other applications of the idea of mutation-as-data:
- Transactional databases often use write-ahead log (WAL) to help atomicity of transactions. Database writs all mutations into WAL. Then after some time the mutations in WAL will be merged to base data in disk.
- Event sourcing. Derive the latest state from events and previous checkpoint. Distributes systems often use consensus protocol (like Raft) to replicate log (events, mutations). The mutable data is derived from logs and previous checkpoint.
- The idea of turning operations into data is also adopted by io_uring and modern graphics APIs (Vulkan, Metal, WebGPU).
- The idea of turning mutation into insertion is also adopted by ClickHouse. In ClickHouse, direct mutaiton is not performant. Mutate-by-insert is faster, but querying require aggregate both the old data and new mutations.
- In modern CPUs, writing to memory is (often) appending data to store buffer. The actual memory write is delayed and batched.
Avoid in-place mutation
The previous problem can be avoided if you don't do in-place mutation.
One ways is mutate-by-recreate: The data is immutable. When you want to mutate something, you create a new version of it. It's widely used in functional programming.
Sometimes transforming is better than mutating. Instead of mutating in-place, consume old state and compute new state.
The old state can use different type than new state, which can improve type safety (Typestate pattern). For example, if it has an Option<T> field that need to be filled in a function, separate input and output as two types, the input type don't have that field, the output has that field of type T (not Option<T>). This can avoid .unwrap(). (Its downside is that you may duplicate some fields and have more types.)
Not doing in-place mutation can reduce chance of bugs. In OOP languages it's easy to wrongly share mutable object. Mutating a wrongly-shared object may cause bugs. Rust helps reducing these bugs.
Mutate-by-recreate is contagious up to parent: if you recreated a new version of a child, you need to also recreate a new version of parent that holds the new child, and parent's parent, and so on, until a "mutable root". There are abstractions like lens to make this kind of cascade-recreate more convenient.
Mutate-by-recreate can be useful for cases like:
- Safely sharing data in multithreading (read-copy-update (RCU), copy-on-write (COW)). Only make one "root reference" be mutable atomically. Mutating is recreating whole object. (It usually requires deferred desctuction, arc_swap)
- Take snapshot and rollback efficiently
Persistent data structure: they share unchanged sub-structure (structural sharing) to make mutate-by-recreate faster. Some crates of persistent data structures: rpds, im, pvec.
Example of mutating hash map while looping on a clone of it, using rpds:
let mut map: HashTrieMap<i32, i32> = HashTrieMap::new();
map = map.insert(2, 3);
for (k, v) in &map.clone() {
if *v > 2 {
map = map.insert(*k * 2, *v / 2);
}
}
Split borrow
Split borrow of fields in struct: As previously mentioned, if you separately borrow two fields of a struct within one scope (e.g. a function), Rust will do a split borrow. This can solve contagious borrow issue. Getter and setter functions break split borrow, because borrowing information become coarse-grained in function signature.
Contagious borrow can also happen in containers. If you borrow one element of a container, then another element cannot be mutably borrowed. How to split borrow a container:
- For
Vecand slice, usesplit_at_mut - For
HashMap, useget_disjoint_mut - For
BTreeMap, the standard library doesn't provide a way. 5
Avoid iterator. Manually manage index (key) in loop
For looping on container is very common. Rust provides concise container for-loop syntax for x in &container {...}. However, it has an implicit iterator that keeps borrowing the whole container.
One solution is to manually manage index (key) in loop, without using iterator. For Vec or slice, you can make index a mutable local variable, then use while loop to traverse the array.
The previous example rewritten using manual loop:
pub struct Parent {
total_score: u32,
children: Vec<Child>
}
pub struct Child { score: u32 }
impl Parent {
fn get_children(&self) -> &Vec<Child> { &self.children }
fn add_score(&mut self, score: u32) { self.total_score += score; }
}
fn main() {
let mut parent = Parent{total_score: 0, children: vec![Child{score: 2}]};
let mut i: usize = 0;
while i < parent.get_children().len() {
let score = parent.get_children()[i].score;
parent.add_score(score);
i += 1;
}
}
It calls .get_children() many times. Each time, the result borrow is kept for only a short time. After copying the score field of element, it stops borrowing the element, which then indirectly stops borrowing the parent.
Note that it requires stop borrowing the element before doing mutation. That example copies score integer so it can stop borrowing the child. For other large data structures, you also need copying/cloning to stop borrowing element (reference counting and persistent data structure can reduce cost of cloning).
(Rust doesn't have C-style for loop for (int i = 0; i < len; i++).)
The similar thing can be done in BTreeMap. We can get the minimum key, then iteratively get next key. This allows looping on BTreeMap without keep borrowing it.
Example of mutating a BTreeMap when looping on it.
let mut map: BTreeMap<i32, i32> = BTreeMap::new();
map.insert(2, 3);
let mut curr_key_opt: Option<i32> = map.first_key_value().map(|(k, _v)| *k);
while let Some(current_key) = curr_key_opt {
let v: &i32 = map.get(¤t_key).unwrap();
if *v > 2 {
map.insert(current_key * 2, *v / 2);
}
curr_key_opt = map.range((Bound::Excluded(¤t_key), Bound::Unbounded))
.next().map(|(k, _v)| *k);
}
Note that it requires copying/cloning the key, and stop borrowing element before mutating.
That way doesn't work for HashMap. HashMap doesn't preserver order and doesn't allow getting the next key. But that way can work on indexmap's IndexMap, which allows getting key by integer index (it internally uses array, so removing or adding in the middle is not fast).
Just (shallow) clone the data
Cloning data can avoid keeping borrowing the data. For immutable data, wrapping in Rc (Arc) then clone can work:
The previous example rewritten by wrapping container in Rc then for-loop:
pub struct Parent {
total_score: u32,
children: Rc<Vec<Child>>
}
pub struct Child {
score: u32
}
impl Parent {
fn get_children(&self) -> Rc<Vec<Child>> {
self.children.clone()
}
fn add_score(&mut self, score: u32) {
self.total_score += score;
}
}
fn main() {
let mut parent = Parent{total_score: 0, children: Rc::new(vec![Child{score: 2}])};
for child in parent.get_children().iter() {
parent.add_score(child.score);
}
}
For mutable data, to make cloning and mutation more efficient, the previously mentioned persistent data structure can be used.
If the data is small, deep cloning is usually fine. If it's not in hot code, deep cloning is also usually fine.
For container contagious borrow, a solution is to firstly copy the keys to a new container then use keys to access the container.
There is a misconception: "I already choosed Rust. So I must optimize performance to justify 'Rust cost'. I must not do unnecessary copy." The performance follows 80/20 rule. 80% of time is spent executing 20% code 6. If some code is not bottleneck, optimizing it has neglegible effect. Only optimize after knowing bottleneck. Also performance is not the sole reason of using Rust (e.g. avoid data race Heisenbug).
Contagious borrowing between branches
It's a common pattern that we cache some things using a map. If the element is not in cache, we compute it and put into map.
We want the borrow the value in cache to avoid cloning the value:
fn get_cached_result(cache: &mut HashMap<i32, String>, key: i32) -> &String {
match cache.get(&key) {
None => {
let computed_value = "assume this is result of computation".to_string();
cache.insert(key, computed_value);
cache.get(&key).unwrap() // value is moved into map so get again
}
Some(v) => {v}
}
}
It triggers contagious borrow between branches:
error[E0502]: cannot borrow `*cache` as mutable because it is also borrowed as immutable
--> src\main.rs:9:13
|
5 | fn get_cached_result(cache: &mut HashMap<i32, String>, key: i32) -> &String {
| - let's call the lifetime of this reference `'1`
6 | match cache.get(&key) {
| ----- immutable borrow occurs here
...
9 | cache.insert(key, computed_value);
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ mutable borrow occurs here
...
12 | Some(v) => {v}
| - returning this value requires that `*cache` is borrowed for `'1`
In Rust, expressions can output a value. In that case the match expression outputs a value. That match has two branches. Each branch also output a value.
Because the match target cache.get(&key) indirectly borrows cache mutably. And the second branch Some(v) => {v}'s output indirectly borrow match target. This indirect borrow of cache is contagious to the whole match expression. In cache.insert it also mutably borrows cache so it conflicts.
One workaround: firstly use containes_key to check whether should insert. After that, read from the map again:
fn get_cached_result(cache: &mut HashMap<i32, String>, key: i32) -> &String {
if !cache.contains_key(&key) {
let computed_value = "assume this is result of computation".to_string();
cache.insert(key, computed_value);
}
cache.get(&key).unwrap()
}
The contains_key gives a bool that doesn't borrow anything. The branch also has no output value now.
That solution is not elegant because both contains_key and get lookups the map. If cache hits it lookups twice but it actually only need once. (The extra cost may can be optimized out by compiler).
A more elegant solution is to use entry API:
fn get_cached_result(cache: &mut HashMap<i32, String>, key: i32) -> &String {
cache.entry(key).or_insert_with(|| {
"assume this is result of computation".to_string()
})
}
(The entry API was specifically designed to workaround this borrow checker limitation.)
This will be fixed by Polonius borrow checker. Currently (2025 Aug) it's available in nightly Rust and can be enabled by an option. See also
That issue can also be workarounded by cloning value in map.
Clarifications about branch contagious borrow
The actual mechanism of that issue not simple. Some clarifications:
This issue only occurs when one branch's output indirectly borrows matched value. If the matched value (condition of if) don't indirectly borrow, then two branches don't interfere. Two branches can both borrow cache without interference:
If the output don't indirectly borrow from matched value it can compile:
fn get_cached_result(cache: &mut HashMap<i32, String>, key: i32) -> &String {
match cache.get(&key) {
None => {
let computed_value = "assume this is result of computation".to_string();
cache.insert(key, computed_value);
cache.get(&key).unwrap()
}
Some(v) => {
// v is not used, can workaround the issue
cache.get(&key).unwrap()
}
}
}
Rust has "indirect borrow". If a contains a borrow into b then a indirectly borrows b. To avoid use-after-free, Rust will ensure b lives when a lives.
In that case the cache.get(&key) indirectly borrows cache. The Some(v) indirectly borrows cache.get(&key). v also indirectly borrow cache.get(&key) which indirectly borrows cache.
If v may be output of match expression, then whole match expression indirectly borrow cache. But if v cannot be output of match expression, then that issue doesn't apply. Triggering that issue requires a "chain" of indirect borrows.
The issue applies not only to match. The issue also applies to if let, which is also pattern match.
The issue doesn't apply to normal if, because normal if can only test on bool which cannot indirectly borrow anything.
Callbacks
Callbacks are commonly used in GUIs, games and other dynamic reactive systems. If parent want to be notified when some event happens on child, the parent register callback to child, and child calls callback when event happens.
However, the callback function object often have to reference the parent (because it need to use parent's data). Then it creates circular reference: parent references child, child references callback, callback references parent. This creates trouble as Rust is unfriendly to circular reference.
Summarize solutions to circular reference callbacks:
- Pass mutable data in argument. Don't make the callback capture mutable data. This can break the circular reference.
- Turn events into data. Use ID/handle to refer to objects. Don't use callback. Just create events and process events.
- (Not recommended) Use reference counting and interior mutability, like
Rc<RefCell<>>.
For example, in a GUI application, I have a counter and a button, clicking button increments counter:
struct ParentComponent {
button: ChildButton,
counter: u32,
}
struct ChildButton {
on_click: Option<Box<dyn FnMut() -> ()>>,
}
fn main() {
let mut parent = ParentComponent {
button: ChildButton { on_click: None },
counter: 0
};
parent.button.on_click = Some(Box::new(|| {
parent.counter += 1;
}));
}
Compile error
error[E0597]: `parent.counter` does not live long enough
--> src\main.rs:19:9
|
13 | let mut parent = ParentComponent {
| ---------- binding `parent` declared here
...
18 | parent.button.on_click = Some(Box::new(|| {
| - -- value captured here
| ___________________________________|
| |
19 | | parent.counter += 1;
| | ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ borrowed value does not live long enough
20 | | }));
| |______- coercion requires that `parent.counter` is borrowed for `'static`
21 | }
| - `parent.counter` dropped here while still borrowed
|
= note: due to object lifetime defaults, `Box<dyn FnMut()>` actually means `Box<(dyn FnMut() + 'static)>`
Replace capturing with argument
The callback need to access the mutable state. The callback can access data in 3 ways:
- Arguments.
- Capturing. It stores data inside function object.
- Global variable. It's not recommended (only use when really necessary).
Use capturing to make callback access mutable data creates circular reference. Letting callback to access mutable data via argument suits borrow checker better.
We can pass the mutable state as argument to callback, instead of letting callback capture it:
struct ParentState {
counter: u32,
}
struct ParentComponent {
button: ChildButton,
state: ParentState,
}
struct ChildButton {
on_click: Option<Box<dyn Fn(&mut ParentState) -> ()>>,
}
fn main() {
let mut parent = ParentComponent {
button: ChildButton { on_click: None },
state: ParentState { counter: 0 },
};
parent.button.on_click = Some(Box::new(|state| {
state.counter += 1;
}));
// it does a split borrow of two fields in parent
parent.button.on_click.unwrap()(&mut parent.state);
assert!(parent.state.counter == 1);
}
That method is useful when callback needs to share mutable data, not just for circular reference.
Avoid callback. Defer event handling. Event-as-data.
Apply the previous deferred mutation and mutation-as-data idea. Don't immediately call callback when event happens. Store events as data and put to a queue.
The event should use ID/handle to refer to data, without indirectly borrowing the mutable data. The event then can be notified to the components that subscribe to specific event channels. Event can be handled in a top-down manner, following ownership tree.
Incomplete code example:
enum Event {
ButtonClicked { button_id: Uuid },
// ...
}
struct ParentComponent {
id: Uuid,
button: ChildButton,
counter: u32,
}
struct ChildButton {
id: Uuid,
}
impl ParentComponent {
fn handle_event(&mut self, event: Event) -> bool {
match event {
Event::ButtonClicked { button_id } if button_id == self.button.id => {
self.counter += 1;
true
}
_ => false,
}
}
}
... // many code omitted
In backend applications, it's common to use external message broker (e.g. Kafka) to pass message. Using them also requires turning event into data.
Other circular references
Grouping two things together can create circular reference:
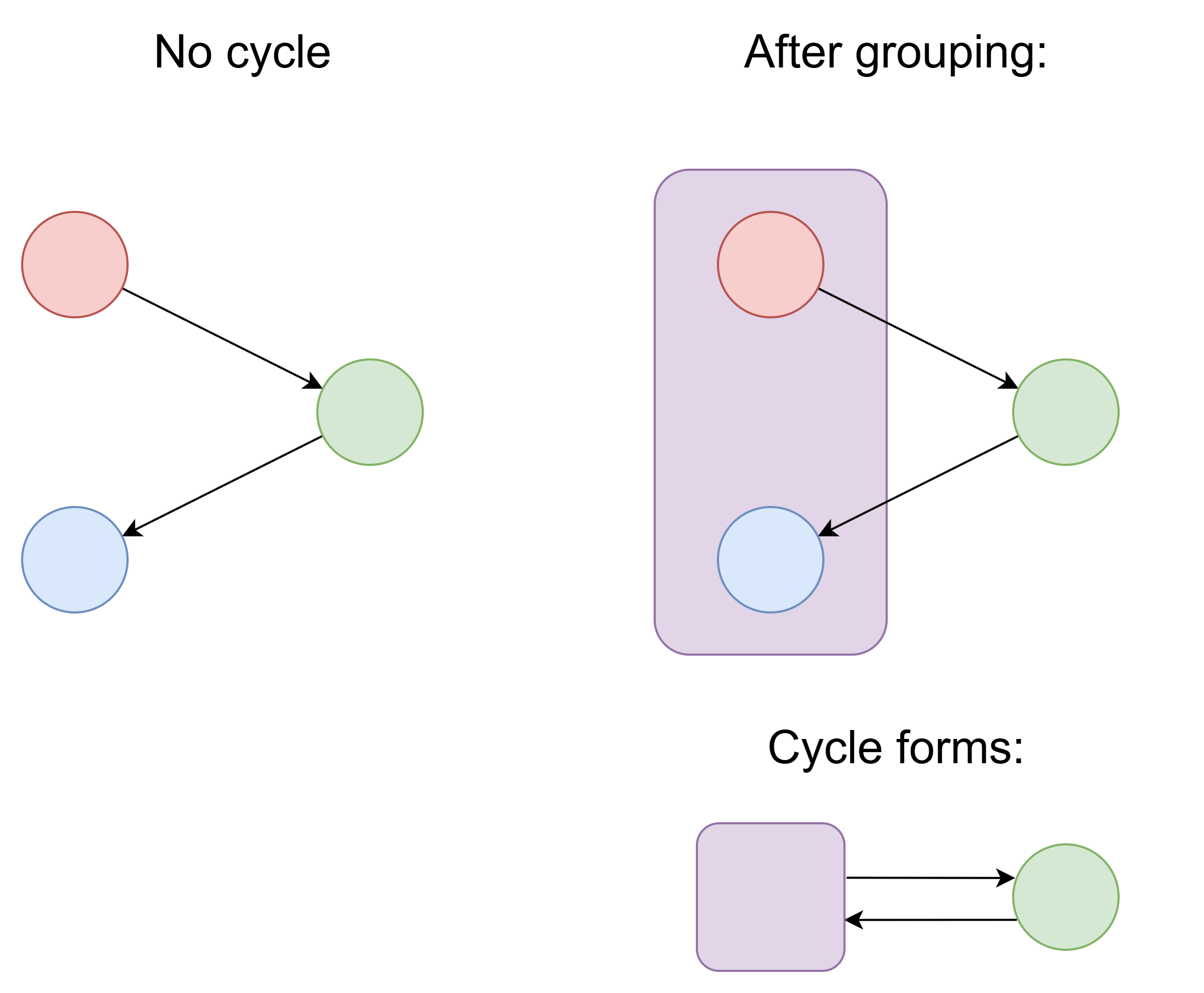
It's similar to contagious borrow issue. Putting two things into one struct can create new circular reference, which is unfriendly to borrow checker. No need to put one object's all data into one struct. One object's data can be scattered in many places.
In OOP languages, it's a common pattern that parent references child, and child references parent. It's convenient because you can access parent data in child's method, without passing parent as argument. That creates circular reference.
However, Rust is unfriendly to circular reference, so the just-for-convenience circular reference should be avoided. It's recommended to pass extra arguments instead of having circular reference.
Note that due to previously mentioned contagious borrow issue, you cannot mutably borrow child and parent at the same time. One workaround is to do a split borrow on parent and pass the individual components of parent (pass more arguments, it's less convenient).
In a tree structure, letting child node to reference parent node can be convenient. If you get a reference to a node, it's easy to do things that use parent data. One workaround is to keep tracking the path from root node to current node (but that solution is unfriendly to mutation). A better solution is to use ID/handle to replace borrow.
In C++ there is the unregister-from-parent-on-destruct pattern: the parent keep a container of child object pointers; in child object's destructor, it removes itself from parent's container. This pattern also involves circular reference. This should be avoided in Rust. The child should be owned by parent, and destructing child should be done via parent.
Although circular reference is convenient in GC languages, it still has memory leak risk: when every child references parent, keeping a reference to one node of whole structure will prevent the whole structure from being GCed. In GC languages, the capturing of closure (lambda expression) are one common source of memory leaks, as the capturing is not obvious 7.
The circular reference that's inherent in data structure
If the data structure inherently requires circular reference, solutions:
- Use arena. Use ID/handle to replace borrow (elaborated later).
- Use reference counting and interior mutability (not recommended).
- Use
unsafe(only use if really necessary).
Self-reference
Self-reference means a struct contains an interior pointer to another part of its own data.
Some crates for providing safe interface of using self-reference:
There is Pin for avoiding an object from being moved in memory. Normal Rust mutable borrow allow moving the value out (by mem::replace, or mem::swap, etc.). Pin is hard to use. If you have a pinned object reference, you cannot get the pinned field reference without unsafe, unless using pin_project. Also auto reborrow doesn't work for Pin.
The problems of Pin aim to be solved in Move trait and in-place initialization.
Pin also appears in futures. Because an async function may have a local variable reference another local variable, and local variables can be put into Future state machines, so the Future will have self-reference.
Use handle/ID to replace borrow
Data-oriented design:
- Try to pack data into contagious array, (instead of objects laid out sparsely managed by allocator).
- Use handle (e.g. array index) or ID to replace reference.
- Decouple object ID with memory address. An ID can be saved to disk and sent via network, but a pointer cannot (the same address cannot be used in another process or after process restart, because there may be other data in the same address).
- The different fields of the same object doesn't necessarily need to be together in memory. The one field of many objects can be put together (parallel array).
- Manage memory based on arenas.
Some may think that using handle/ID is "just a nasty workaround caused by borow checker". However, in GC languages, using ID to refer to object is also common, as reference cannot be saved to database or sent via network. 8
Arena
One kind of arena is slotmap. It's generational arena.
SlotMap is similar to an array of elements, but each slot has a generation integer. If a slot's element is dropped and new element is placed in same slot, the generation counter increases.
Each handle (key) has an index and a generation integer. It's Copy-able data that's not restricted by borrow checker. Accessing slotmap only succeedes if slot generation matches.
Although memory safe, it still has the equivalent of "use-after-free": using a handle of an already-removed object cannot get element from the slotmap 9. Each get element operation may fail.
Note that SlotMap is not efficient when there are many unused empty space between elements. slotmap crate offers two HopSlotMap and DenseSlotMap for better performance in sparce case.
Other kinds of arenas:
- Other map structure, like
HashMaporTreeMapcan also be arenas. - If no element can be removed from arena, then a
Veccan also be an areana. id-arena attaches extra arena id to key, so that keys of different arenas can never be confused. - generational_box
- bevy_ecs
The important things about arena:
- The borrow checker no longer ensure the ID/handle points to a living object. Each data access to arena may fail. There is equivalent of "use after free".
- Arenas still suffer from contagious borrow issue. Borrowing one element in arena indirectly borrows whole arena. The previously mentioned solutions (deferred mutation, shallow clone, manual container loop, persistent data structure, etc.) may be needed.
Some may think "using arena cannot protect you from equivalent of 'use after free' so it doesn't solve problem". But arena can greatly improve determinism of bugs, making debugging much easier. A randomly-occuring memory safety Heisenbug may no longer trigger when you enable sanitizer, as sanitizer can change memory layout.
About linked list
In Rust, writing a pointer-based linked list is hard. Writing zero-cost pointer-based doubly-linked list in safe Rust is impossible.
But that only applies to pointer-based linked list. The conventional pointer-based linked list often has bad cache locality (because it uses global allocator, nodes may scatter in memory space).
Writing arena-based linked list in Rust is easy. And it can have better cache locality. And you can use 32-bit index instread of 64-bit pointer which also improves cache locality by reducing space usage.
The pointer-based linked list can also be optimized by making one node hold many elements.
Entity component system
Entity component system (ECS) is a way of organizing data that's different to OOP. In OOP, an object's fields are laid together in memory. But in ECS, each object is separated into components. The same kind of components for different entities are managed together (often laid together in memory). It can improve cache-friendliness. (Note that performance is affected by many factors and depends on exact case.)
ECS also favors composition over inheritance. Inheritance tend to bind code with specific types that cannot easily compose.
For example, in an OOP game, Player extends Entity, Enemy extends Entity. There is a special enemy Ghost that ignores collision and also extends Enemy. But one day if you want to add a new player skill that temporarily ignores collision like Ghost, you cannot make Player extend Ghost. Then the logic of ignoring collision has to be lifted into superclass Entity (or duplicated in both Ghost and Player). After many of these, Entity will contain many mixed logic, which defeats abstraction. In ECS it can be solved by just changing collision component.
Mutable borrow exclusiveness
As previously mentioned, Rust has mutable borrow exclusiveness:
- A mutable borrow to one object cannot co-exist with any other borrow to the same object. Two mutable borrows cannot co-exist. One mutable and one immutable also cannot co-exist.
- Multiple immutable borrows for one object can co-exist.
That is also called "mutation xor sharing", as mutation and sharing cannot co-exist.
In multi-threading case, this is natural: multiple threads read the same immutable data is fine. As long as one thread mutates the data, other thread cannot safely read or write it without other synchronization (atomics, locks, etc.).
But in single-threaded case, this restriction is not natural at all. No mainstream language (other than Rust) has this restriction.
Mutation xor sharing is, in some sense, neither necessary nor sufficient. It’s not necessary because there are many programs (like every program written in Java) that share data like crazy and yet still work fine. It’s also not sufficient in that there are many problems that demand some amount of sharing – which is why Rust has “backdoors” like
Arc<Mutex<T>>,AtomicU32, and—the ultimate backdoor of them all—unsafe.
Mutable borrow exclusiveness is still important for safety of interior pointer, even in single thread:
Interior pointer
Rust has interior pointer. Interior pointer are the pointers that point into some data inside another object. A mutation can invalidate the memory layout that interior pointer points to.
For example, you can take pointer of an element in Vec. If the Vec grows, it may allocate new memory and copy existing data to new memory, thus the interior pointer to it can become invalid (break the memory layout that interior pointer points to). Mutable borrow exclusiveness can prevent this issue from happening:
fn main() {
let mut vec: Vec<u32> = vec!(1, 2, 3);
let interior_pointer: &u32 = &vec[0];
vec.push(4);
print!("{}", *interior_pointer);
}
Compile error:
3 | let interior_pointer: &u32 = &vec[0];
| --- immutable borrow occurs here
4 | vec.push(4);
| ^^^^^^^^^^^ mutable borrow occurs here
5 | print!("{}", *interior_pointer);
| ----------------- immutable borrow later used here
Another example is about enum: interior pointer pointing inside enum can also be invalidated, because different enum variants has different memory layout. In one layout the first 8 bytes is integer, in another layout the first 8 bytes may be a pointer. Treating an arbitrary integer as a pointer is definitely not memory-safe.
enum DifferentMemoryLayout {
A(u64, u64),
B(String)
}
fn main() {
let mut v: DifferentMemoryLayout = DifferentMemoryLayout::A(1, 2);
let interior_pointer: &u64 = match v {
DifferentMemoryLayout::A(ref a, ref b) => {a}
DifferentMemoryLayout::B(_) => { panic!() }
};
v = DifferentMemoryLayout::B("hello".to_string());
println!("{}", *interior_pointer);
}
Compile error:
9 | DifferentMemoryLayout::A(ref a, ref b) => {a}
| ----- `v` is borrowed here
...
12 | v = DifferentMemoryLayout::B("hello".to_string());
| ^ `v` is assigned to here but it was already borrowed
13 | println!("{}", *interior_pointer);
| ----------------- borrow later used here
Note that sometimes mutating can keep validity of interior pointer. For example, changing an element in Vec<u32> doesn't invalidate interior pointer to elements, because there is no memory layout change. But Rust by default prevents all mutation when interior pointer exists (unless using interior mutability).
Interior pointer in other languages
Golang also supports interior pointer, but doesn't have such restriction. For example, interior pointer into slice:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
slice := []int{1, 2, 3}
interiorPointer := &slice[0]
slice = append(slice, 4)
fmt.Printf("%v\n", *interiorPointer)
fmt.Printf("old interior pointer: %p new interior pointer: %p\n", interiorPointer, &slice[0])
}
Output
1
old interior pointer: 0xc0000ac000 new interior pointer: 0xc0000ae000
Because after re-allocating the slice, the old slice still exists in memory (not immediately freed). If there is an interior pointer into the old slice, the old slice won't be freed by GC. The interior pointer will always be memory-safe (but may point to stale data).
Golang also doesn't have sum type, so there is no equivalent to enum memory layout change in the previous Rust example.
Also, Golang's doesn't allow taking interior pointer to map entry value, but Rust allows. Rust's interior pointer is more powerful than Golang's.
In Java, there is no interior pointer. So no memory safety issue caused by interior pointer.
But in Java there is one thing logically similar to interior pointer: Iterator. Mutating a container can cause iterator invalidation:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
Iterator<Integer> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer value = iterator.next();
if (value < 3) {
list.remove(0);
}
}
}
}
That will get java.util.ConcurrentModificationException. Java's ArrayList has an internal version counter that's incremented every time it changes. The iterator code checks concurrent modification using version counter.
Even without the version check, it will still be memory-safe because array access is range-checked.
Note that the container for loop in java internally use iterator (except for raw array). Inserting or removing to the container while for looping can also cause iterator invalidation.
Note that iteration invalidation is logic error, no matter whether it's memory-safe or not.
In Java, you can remove element via the iterator, then the iterator will update together with container, and no longer invalidate. Or use removeIf that avoids managing iterator.
Mutable borrow exclusiveness is still important in single-threaded case, because of interior pointer. But if we don't use any interior pointer, then mutable borrow exclusiveness is not necessary for memory safety in single-thread case.
That's why mainstream languages has no mutable borrow exclusiveness, and still works fine in single-threaded case. Java, JS and Python has no interior pointer. Golang and C# have interior pointer, they have GC and restrict interior pointer, so memory safe is still kept without mutable borrow exclusiveness.
Benefits of mutable borrow exclusiveness
Rust's mutable borrow exclusiveness creates a lot of troubles in single-threaded cases. But it also has benefits (even in signle-threaded cases):
- Make the borrow more universal. In Rust, map key and value can be borrowed. But in Golang you cannot take interior pointer to map key or value. This makes abstractions that work with borrows more general.
- Mutable borrow is exclusive, so Rust can emit
noaliasattribute to LLVM.noaliasmeans the pointed data cannot be accessed by other code, which means:- It allows aggressively merging reads. Before next write to it, it can be temporarily treated as constant.
- It allows aggressively merging writes. If there are two memory writes to it, compiler can remove the first write, only keep the last write.
- It allows removing reads after write, using the previous write as read result.
- It allows aggressively reordering reads/writes to it between other computation and other memory accesses.
- The above give compiler a lot of freedom of transforming code, which enables many other optimizations.
- Without
noalias, the optimizer must consider all possible reads/writes to the same value to do above transformation. In many cases, compiler don't have enough information, so much fewer optimizations can be done.
Interior mutability summary
Mutable borrow exclusiveness is overly restrictive. It is not necessary for memory safety in single-threaded code when not using interior pointer. There is interior mutability that allows getting rid of that constraint.
Interior mutability allows you to mutate something from an immutable reference to it. (Because of that, immutable borrow doesn't necessarily mean the pointed data is actually immutable. This can cause some confusion.)
Ways of interior mutability:
Cell<T>. It's suitable for simple copy-able types like integer.RefCell<T>, suitable for data structure that does incremental mutation, in single-threaded cases. It has internal counters tracking how many immutable borrow and mutable borrow currently exist. If it detects violation of mutable borrow exclusiveness,.borrow()or.borrow_mut()will panic.It can cause crash if there is nested borrow that involves mutation.Mutex<T>RwLock<T>, for locking in multi-threaded case. Its functionality is similar toRefCell. Note that unnecessary locking can cost performance, and has risk of deadlock. It's not recommended to overuseArc<Mutex<T>>just because it can satisfy the borrow checker.QCell<T>. Elaborated below.- Atomic types such as
AtomicU32 UnsafeCell<T>- Lazily-initialized
OnceCell<T> - ......
They are usually used inside reference counting (Arc<...>, Rc<...>).
RefCell is not panacea
In the previous contagious borrow case, wrapping parent in RefCell<> can make the code compile. However it doesn't fix the issue. It just turns compile error into runtime panic:
use std::cell::RefCell;
pub struct Parent { total_score: u32, children: Vec<Child> }
pub struct Child { score: u32 }
impl Parent {
fn get_children(&self) -> &Vec<Child> {
&self.children
}
fn add_score(&mut self, score: u32) {
self.total_score += score;
}
}
fn main() {
let parent: RefCell<Parent> = RefCell::new(Parent{total_score: 0, children: vec![Child{score: 2}]});
for child in parent.borrow().get_children() {
parent.borrow_mut().add_score(child.score);
}
}
It will panic with RefCell already borrowed error.
RefCell still follows mutable borrow exclusiveness rule, just checked at runtime, not compile time. Borrowing one field inside RefCell still borrows the whole RefCell.
Wrapping parent in RefCell cannot fix contagious borrow, but putting individual children into RefCell can work, as it makes borrow more fine-grained.
See also: Dynamic borrow checking causes unexpected crashes after refactorings
Rust assumes that, if you have a mutable borrow &mut T, you can use it at any time. But holding the reference is different to using reference. There are use cases that I have two mutable references to the same object, but I only use one at a time. This is the use case that RefCell solves.
Another problem: The borrow taken from RefCell cannot be directly returned.
pub struct Parent {
entries: RefCell<HashMap<String, Entry>>,
...
}
pub struct Entry { score: u32 }
impl Parent {
fn get_entries(&self) -> &HashMap<String, Entry> {
self.entries.borrow()
}
...
}
Compile error:
error[E0308]: mismatched types
--> src\main.rs:10:9
|
9 | fn get_entries(&self) -> &HashMap<String, Entry> {
| ----------------------- expected `&HashMap<String, Entry>` because of return type
10 | self.entries.borrow()
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ expected `&HashMap<String, Entry>`, found `Ref<'_, HashMap<String, Entry>>`
|
= note: expected reference `&HashMap<_, _>`
found struct `Ref<'_, HashMap<_, _>>`
help: consider borrowing here
|
10 | &self.entries.borrow()
| +
Because the borrow got from RefCell is not normal borrow, it's actually Ref. Ref implements Deref so it can be used similar to a normal borrow.
The "help: consider borrowing here" suggestion won't solve the compiler error. Don't blindly follow compiler's suggestions.
One solution is to return &RefCell<HashMap<String, Entry>>. Then RefCell "invades" the getter signature and make abstraction leaky. (Returning Ref<HashMap<String, Entry>> or impl Deref<Target=HashMap<String, Entry>> can also work but all not good.)
Rc<RefCell<...>> and Arc<Mutex<...>> are not panacea
Rc<RefCell<...>> and Arc<Mutex<...>> allows freely copying reference and freely mutating things, just like in other languages. Finally "get rid of shackle of borrow checker". However, there are traps:
- Contagious borrowing. As previously mentioned,
RefCellwrapping parent doesn't solve contagious borrowing.Mutexalso won't. Violating mutable borrow exclusiveness in the same thread is panic (or error) inRefCelland deadlock inMutex. Rust lock is not re-entrant, explained below. - Need to cut cycle using
Weak, unless it will memory leak. - Performance.
RcandRefCellhas relatively small performance cost. But forArc<Mutex<...>>, unnecessary locking can hurt performance.Arcalso can have performance issue, explained below. It's still ok to use them when not in performance bottleneck. - Their syntax ergonomic is not good. The code will have a lot of "noise" like
.borrow().borrow_mut().
This doesn't mean Arc<Mutex<>> shouldn't be used. It should be used when you want both sharing and locking. It should not be used for just evading borrow checker restriction.
QCell
QCell<T> has an internal ID. QCellOwner is also an ID. You can only use QCell via an QCellOwner that has matched ID.
The borrowing to QCellOwner "centralizes" the borrowing of many QCells associated with it, ensuring mutable borrow exclusiveness. Using it require passing borrow of QCellOwner in argument everywhere it's used.
QCell will fail to borrow if the owner ID doesn't match. Different to RefCell, if owner ID matches, it won't panic just because of nested borrow.
Its runtime cost is low. When borrowing, it just checks whether cell's id matches owner's id. It has memory cost of owner ID per cell.
One advantage of QCell is that the duplicated borrow will be compile-time error instead of runtime panic, which helps catch error earlier. If I change the previous RefCell panic example into QCell:
pub struct Parent { total_score: u32, children: Vec<Child> }
pub struct Child { score: u32 }
impl Parent {
fn get_children(&self) -> &Vec<Child> { &self.children }
fn add_score(&mut self, score: u32) { self.total_score += score; }
}
fn main() {
let owner: QCellOwner = QCellOwner::new();
let parent: QCell<Parent> = QCell::new(&owner, Parent{total_score: 0, children: vec![Child{score: 2}]});
for child in parent.ro(&owner).get_children() {
parent.rw(&mut owner).add_score(child.score);
}
}
Compile error:
17 | for child in parent.ro(&owner).get_children() {
| --------------------------------
| | |
| | immutable borrow occurs here
| immutable borrow later used here
18 | parent.rw(&mut owner).add_score(child.score);
| ^^^^^^^^^^ mutable borrow occurs here
It turns runtime panic into compile error, which make discovering problems eariler.
GPUI's Model<T> is similar to Rc<QCell<T>>, where GPUI's AppContext correspond to QCellOwner.
Directly using Arc<QCell<>> is not convenient. GPUI has many wrappers that make it more convenient.
It can also work in multithreading, by having RwLock<QCellOwner>. This can allow one lock to protect many pieces of data in different places 10.
Ghost cell and LCell are similar to QCell, but use closure lifetime as owner id. They are zero-cost, but more restrictive (owner is tied to closure scope, cannot dynamically create, owner cannot outlive closure).
Note that QCell still suffers from contagious borrow: after mutably borrowing one QCell under a QCellOwner, you cannot borrow another QCell under the same QCellOwner, except when using special multi-borrow like rw2.
Rust lock is not re-entrant
Re-entrant lock means one thread can lock one lock, then lock it again, then unlock twice, without deadlocking. Rust lock is not re-entrant. (Rust lock is also responsible for keeping mutable borrow exclusiveness. Allowing re-entrant can produce two &mut for same object.)
For example, in Java, the two-layer locking doesn't deadlock:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object lock = new Object();
synchronized (lock) {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("within two layers of locking");
}
}
System.out.println("finish");
}
}
But in Rust the equivalent will deadlock:
fn main() {
let mutex: Mutex<u64> = Mutex::new(0);
{
let mut g1: MutexGuard<u64> = mutex.lock().unwrap();
{
println!("going to do second-layer lock");
let mut g2 = mutex.lock().unwrap();
println!("within two layers of locking");
}
}
println!("finish");
}
It prints going to do second-layer lock then deadlocks.
In Rust, it's important to be clear about which scope holds lock. Golang lock is also not re-entrant.
Another important thing is that Rust only unlocks at the end of scope by default. mutex.lock().unwrap() gives a MutexGuard<T>. MutexGuard implements Drop, so it will drop at the end of scope. It's different to the local variables whose type doesn't implement Drop, they are dropped after their last use (unless borrowed). This is called NLL (non-lexical lifetime).
Arc is not always fast
Arc uses atomic operations to change its reference count. (Cloning and dropping Arc changes reference count, but borrowing Arc doesn't.)
However, when many threads frequently change the same atomic counter, performance can degrade. The more threads touching it, the slower it is.
Modern CPUs use cache coherency protocol (e.g. MOESI). Atomic operations often require the CPU core to hold "exclusive ownership" to cache line (this may vary between different hardware). Many threads frequently doing so cause cache contention, similar to locking, but on hardware.
Using Arc wrongly may result in slower performance than using GC languages. In GC languages, reading an on-heap reference often only involve a simple memory read 11, without atomic read-modify-write operation.
Atomic reference counting is still fast if not contended (mostly only one thread change reference count). Atomic reference counting is faster on Apple silicon than Intel CPUs. 12
Solutions:
- Avoid sharing the same reference count. Copying data is sometimes better.
- trc and hybrid_rc. They use per-thread non-atomic counter, and another shared atomic counter for how many threads use it. This can make atomic operations be less frequent, getting higher performance.
- For scenario of frequent short-term reads:
- arc_swap. It uses hazard pointer and other mechanics to improve performance.
- crossbeam_epoch. It uses epoch-based memory reclamation.
- aarc
These deferred memory reclamation techniques (hazard pointer, epoch-based) are also used in lock-free data structures. If one thread can read an element while another thread removes and frees the same element in parallel, it will not be memory-safe (this issue doesn't exist in GC languages).
Note that using Arc doesn't mean every access uses atomic operation. Only cloning and dropping it requires atomic operation. .borrow() it doesn't involve atomic operation. Passing &Arc<T> instead of Arc<T> can improve performance.
This does NOT mean we should avoid using Arc. Only optimize after knowing the bottleneck.
Reference counting vs tracing GC
There are some ambiguity of the word "GC". Some say reference counting is GC, some say it isn't.
No matter what the definition of "GC" is, reference counting is different from tracing GC (in Java/JS/C#/Golang/etc.):
| Reference counting | Tracing GC |
|---|---|
| Frees memory immediately | Frees in deferred and batched way 13 |
| Freeing a whole large structure may cause large lag 14 | Require more memory to achieve high performance, otherwise GC lag will be large. |
| Finds greatest fixed point | Finds least fixed point |
| Propagates "death". (freeing one object may cause its children to be freed) | Propagates "live". (a living object cause its children to live, except for weak reference) |
Cloning and dropping a reference involves atomic operation (except single-threaded Rc) | Reading/writing an on-heap reference may involve read/write barrier (often a branch, no atomic memory access) |
| Cannot automatically handle cycles. Need to use weak reference to cut cycle | Can handle cycles automatically |
| Cost is roughly O(reference count changing frequency) 15 | Cost is roughly O(count of living objects * GC frequency) 16 |
Bump allocator
bumpalo provides bump allocator. In bump allocator, allocation is fast because it usually just increase an integer. It supports quickly freeing the whole arena, but doesn't support freeing individual objects.
It's usually faster than normal memory allocators. Normal memory allocator will do a lot of bookkeeping work for each allocation and free. Each individual memory region can free separately, these regions can be reused for later allocation, these information need to be recorded and updated.
Bump allocator frees memory in batched and deferred way. As it cannot free individual objects, it may temporarily consume more memory.
Bump allocator is suitable for temporary objects, where you are sure that none of these temporary objects will be needed after the work complets.
The function signature of allocation (changed for clarity):
impl Bump {
...
pub fn alloc<T, 'bump>(&'bump self, val: T) -> &'bump mut T { ... }
}
It takes immutable borrow of Bump (it has interior mutability). It moves val into the bump-allocated memory region. It outputs a mutable borrow, having the same lifetime as bump allocator. That lifetime ensures memory safety (cannot make the borrow of allocated value outlive bump allocator).
If you want to keep the borrow of allocated result for long time, then lifetime annotation is often required. In Rust, lifetime annotation is also contagious:
- Every struct that holds bump-allocated borrow need to also have lifetime annotation of the bump allocator.
- Every function that use it also needs lifetime annotation. Rust has lifetime elision, which allows you to omit lifetime in function signature in some cases. However you still need to write a lot of things like
<'_>.
Adding or removing lifetime for one thing may involve refactoring many code that use it, which can be huge work. (AI can help in these kinds of refactoring.)
yoke allows getting rid of lifetime annotation by combining bump-allocated structure together with the bump allocator.
Bump doesn't implement Sync, so &Bump is not Send. It cannot be shared across threads (even if it can share, there will be lifetime constraint that force you to use structured concurrency). It's recommended to have separated bump allocator in each thread, locally.
Putting a Bump with its allocated references together creates self-reference. It's more tricky (can use yoke).
Note that bumpalo by default don't run drop to improve performance. Use bumpalo::boxed::Box<T> for things that require invoking drop.
Using unsafe
By using unsafe you can freely manipulate pointers and are not restricted by borrow checker. But writing unsafe Rust is harder than just writing C, because you need to carefully avoid breaking the constraints that safe Rust code relies on. A bug in unsafe code can cause issue in safe code.
Writing unsafe Rust correctly is hard. Here are some traps in unsafe:
- Don't violate mutable borrow exclusiveness.
- A
&mutshould not overlap with any other borrows and raw pointers. - The overlap here also includes interior pointer. A
&mutto an object cannot co-exist with any other borrow into any part of that object. - Violating that rule cause undefined behavior and can cause wrong optimization. Rust adds
noaliasattribute for mutable borrows into LLVM IR. LLVM will heavily optimize based onnoalias. See also - The above rule doesn't apply to raw pointer
*mut T. - Converting a
&Tto*mut Tthen mutate pointed data is undefined behavior. For that use case, wrapTinUnsafeCell<T>. - It's very easy to accidentally violate that rule when using borrows in unsafe. It's recommended to always use raw pointer and avoid using borrow (including slice borrow) in unsafe code. Related1, Related2
- A
- Pointer provenance.
- For to-heap pointers, different allocations are different provenances. For to-stack pointers, different local variables are different provenances.
- Two pointers created from two provenances is considered to never alias. If their address equals, it's undefined behavior.
- Converting an integer to pointer gets a pointer with no provenance, using that pointer is undefined behavior, unless in these two cases:
- The integer was converted from a pointer using
.expose_provenance()and then integer converts to pointer usingwith_exposed_provenance() - The integer
iis converted to pointer usingp.with_addr(i)(pis another pointer that has provenance). The result has same provenance ofp.
- The integer was converted from a pointer using
- Adding a pointer with an integer doesn't change provenance.
- The provenance is tracked by compiler in compile time. In actual execution, pointer is still integer address that doesn't attach provenance information 17.
- Using uninitialized memory is undefined behavior.
MaybeUninit- Normally a byte has 256 possible values. But in LLVM a byte has 258 possible values. The extra two are 1. uninitialized 2. poison (computed from other undefined behaviors). Like pointer provenance, the two extra values only exist in compile time.
a = bwill drop the original object in place ofa. Ifais uninitialized, then it will drop an unitialized object, which is undefined behavior. Useaddr_of_mut!(...).write(...)Related- Handle panic unwinding. If unsafe code turn data into temporarily-invalid state, you need to make it valid again during unwinding. See also.
- Reading/writing to mutable data that's shared between threads need to use atomic, or volatile access (
read_volatile,write_volatile), or use other synchronization (like locking). If not, optimizer may wrongly merge and reorder reads/writes. Note that volatile access themself doesn't establish memory order (unlike Java/C#volatile). - If the binary data violates the type's constraint, it's undefined behavior. For example,
bool's binary data can only be 0 or 1. Making it 2 is undefined behavior. Creating astrwhose binary data is not valid UTF-8 is also undefined behavior. - If you want to
mem::transmute, it's recommended to use zerocopy which has compile-time checks to ensure memory layout are the same. For simple wrapper types, use#[repr(transparent)]. - A C dynamic library (crate type
cdylib) will embed its own copy of standard library and allocator. One allocation in one dynamic library should not be deallocated in another dynamic library. The global variables and thread local variables can duplicately co-exist. - ......
Modern compilers tries to optimize as much as possible. To optimize as much as possible, the compiler makes assumptions as much as possible. Breaking any of these assumption can lead to wrong optimization. That's why it's so complex. See also
Unfortunately Rust's syntax ergonomics on raw pointer is currently not good:
- If
pis a raw pointer, you cannot writep->field(like in C/C++), and can only write(*p).field - Raw pointer cannot be method receiver (self).
- There is no "raw pointer to slice". You need to manually
.add()pointer and dereference. Bound checking is also manual.
Send and Sync
Rust favors tree-shaped ownership. Each object is owned by exactly one place. If you send tree-shaped data to another thread, only one thread can access it, so it's thread-safe. No data race.
Sending an immutable borrow to another thread is also fine as long as the shared data is actually immutable.
But there are exceptions. One exception is interior mutability. Because of interior mutability, the data pointed by immutable borrow &T may no longer actually be immutable. So Rust prevents sharing &Cell<T> and &RefCell<T> by making Cell<T> and RefCell<T> not Sync. If X is Sync then &X is Send. If X is not Sync then &X is not Send. This prevents Cell and RefCell from being shared across threads.
Rc also has internal shared mutable reference counter. It's not atomic, so Rc cannot be passed between threads. It's neither Send or Sync.
But &Mutex<T> can be shared because lock protects them. Also immutable reference to atomic cells like &AtomicU32 can be shared because of atomicity. Mutex<T> and AtomicU32 are Sync so &Mutex<T> and &AtomicU32 are Send.
There are things that are Sync but not Send, like MutexGuard. If something is already locked, sharing its reference to other threads temporarily is fine. But moving a MutexGuard to another thread is not fine because locking is tied to thread.
Send + 'static
Tokio is a popular async runtime. In Tokio, submitting a task require the future to be Send and 'static.
pub fn spawn<F>(future: F) -> JoinHandle<F::Output>
where
F: Future + Send + 'static,
F::Output: Send + 'static,
-
'staticmeans it's standalone (self-owned). It doesn't borrow temporary things. It can borrow global values (global values will always live when program is running).The spawned future may be kept for a long time. It's not determined whether future will only temporarily live within a scope. So the future need to be
'static. tokio_scoped allows submitting a future that's not'static, but it must be finished within a scope.If the future need to share data with outside, pass
Arc<T>into (not&Arc<T>). -
Sendmeans that the future can be sent across threads. Tokio use work-stealing, which means that one thread's task can be stolen by other threads that currently have no work.Sendis not needed if the async runtime doesn't move future between threads.
Rust converts an async functions into a state machine, which is the future object. In async function, the local variables that are used across await points will become fields in future. If the future is required to be Send then these local variables also need to be Send.
Note that the "static" in C/C++/Java/C# often mean global variable. In Rust its meaning is similar but different. static x still declares global value. Borrows to global values have lifetime 'static. But the standalone values (self-owned, don't borrow temporary things) also have 'static lifetime, although they are not global values and don't live forever.
In Rust 'static just mean its lifetime is not limited to a specific scope. It doesn't necessarily mean it will live forever. 'static is the bottom type 18 of lifetimes, similar to never in TypeScript. It's called 'static just because global values' lifetime is coincidentally also bottom type, so the same naming is reused.
Side effect of extracting and inlining variable
In C and GC languages:
- If a variable is used only once, you can inline that variable. This will only change execution order (except in short-circuit 19).
- Extracting a variable will only change execution order (except when variable is used twice or in short-circuit).
But in Rust it's different.
Lifetime of temporary value
Simply put:
- Putting a temporary value to local variable usually makes it live longer.
- Inlining a local variable usually makes it live shorter.
One example
let c: RefCell<Option<String>> = RefCell::new(Option::Some("hello".to_string()));
let string: &String = c.borrow().as_ref().unwrap();
println!("{}", string);
It will compile error "temporary value dropped while borrowed". Because the result of c.borrow() is a temporary value that doesn't live long enough. Solution is to make it a local variable to live longer:
let c: RefCell<Option<String>> = RefCell::new(Option::Some("hello".to_string()));
let borrowed = c.borrow();
let string: &String = borrowed.as_ref().unwrap();
println!("{}", string);
Not all temporary values need to be put into local variable. Sometimes match, if let can implicitly make temporary value live longer.
In other languages, if a local variable is only used once, it's often ok to inline it. But in Rust inlining a local variable that does borrowing can cause compile error.
Reborrow
Normally mutable borrow &mut T can only be moved and cannot be copied.
But reborrow is a feature that sometimes allow you to use a mutable borrow multiple times. Reborrow is very common in real-world Rust code. Reborrow is not explicitly documented. See also
Example:
fn mutate(i: &mut u32) -> &mut u32 {
*i += 1;
i
}
fn mutate_twice(i: &mut u32) -> &mut u32 {
mutate(i);
mutate(i)
}
That works. Rust will implicitly treat the first mutate(i) as mutate(&mut *i) so that i is not moved into and become usable again.
But extracting the second i into a local variable early make it not compile:
fn mutate_twice(i: &mut u32) -> &mut u32 {
let j: &mut u32 = i;
mutate(i);
mutate(j)
}
7 | fn mutate_twice(i: &mut u32) -> &mut u32 {
| - let's call the lifetime of this reference `'1`
8 | let j: &mut u32 = i;
| - first mutable borrow occurs here
9 | mutate(i);
| ^ second mutable borrow occurs here
10 | mutate(j)
| --------- returning this value requires that `*i` is borrowed for `'1`
The Pin doesn't do auto reborrow.
Move cloned data into closure
tokio::spawn require future to be standalone and doesn't borrow other things ('static).
Passing passing an Arc (that's used later) into moved closure makes closure borrow the Arc. The data that contains borrow is not standalone (not 'static).
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() {
let data: Arc<u64> = Arc::new(1);
let task1_handle = tokio::spawn(async move {
println!("From task: Data: {}", *data);
});
println!("From main thread: Data: {}", *data);
}
Compile error
6 | let data: Arc<u64> = Arc::new(1);
| ---- move occurs because `data` has type `Arc<u64>`, which does not implement the `Copy` trait
7 |
8 | let task1_handle = tokio::spawn(async move {
| ---------- value moved here
9 | println!("From task: Data: {}", *data);
| ---- variable moved due to use in coroutine
...
12 | println!("From main thread: Data: {}", *data);
| ^^^^ value borrowed here after move
Manually clone the Arc<T> and put it into local variable works. It will make the cloned version to move into future:
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() {
let data: Arc<u64> = Arc::new(1);
let data2 = data.clone(); // this is necessary
let task1_handle = tokio::spawn(async move {
println!("From task: Data: {}", *data2);
});
println!("From main thread: Data: {}", *data);
}
The new local variable let data2 = data.clone(); is necessary. When there are many such things, it can be cumbersome to write and read. There is a proposal on improving syntax ergonomic of it.
Nuance of "immutable"
There are 3 kinds of "immutable":
- Fully-immutable. The referenced object is immutable, and the reference is also immutable.
- Mutable-ref-to-immutable-obj. The referenced object is immutable, but the reference itself is mutable.
- Immutable-ref-to-mutable-obj. The referenced object is mutable, but the reference itself is immutable.
Note that read-only is different to immutable.
Examples:
- Java
finalreference ensures reference itself is immutable. If pointed object is mutable then its's immutable-ref-to-mutable-obj. - Java
Collections.unmodifiableList()gives read-only view. - Copy-on-write (COW) and read-copy-write (RCU) are mutable-ref-to-immutable-obj.
- Rust
let x: Tmakesxfully immutable. Immutability applies to whole ownership tree. If aVecis immutable, its elements are also immutable. - Rust
let mut x: &Tmakesxa mutable-ref-to-immutable-obj. - Rust
let x: &mut Tmakesxan immutable-ref-to-mutable-obj. - Rust
let x: &mut &[u8]makesxan immutable-ref-to-mutable-slice-ref-to-immutable-binary-data (this is sometimes used in binary data parsing):[u8]is slice of binary data. It's a variable-sized type.&[u8]is slice ref, containing a pointer and a length.mut &[u8]is mutable slice ref. The pointer and length is mutable, but binary data in slice is immutable.xis a pointer to that mutable slice ref.xitself is immutable.
- In Rust, when using interior mutability, an immutable thing can be actually mutable.
- Git release tag is mutable-ref-to-immutable-obj. The Git commit with specific hash is immutable. But Git allows removing a release tag and create a new same-named release tag to another commit. This can be disabled.
String types
In GC languages, strings are simple. There is often one commonly-used immutable string type (String in java, string in JS). But in Rust there are many string types:
str, a variable-sized type. Its content should be valid UTF-8.&str, a borrow tostr. It contains a pointer and a length.String.It also has a pointer and a length (and a capacity number). It heap-allocates the binary data and owns binary data.&strborrows binary data from elsewhere.OsString/OsStr. These exist because Rust string enforces UTF-8 encoding, but operating systems APIs can use non-UTF-8 string. In Linux, file name can be invalid UTF-8. In Windows APIs, strings use encoding similar to UTF-16 but allows invalid surrogates (technically called WTF-16).CString/CStr. C-style null-terminated string. Used for interop with C library.
In C++ and Golang, strings are just binary data with no encoding constraint. Rust enforces UTF-8 and makes it more complex. But enforcing UTF-8 has benefits: no need to worry about encoding mismatch within Rust program. It also improves security because many text processing code assumes string is valid UTF-8, e.g. CVE-2024-56732, CVE-2026-0810.
Using unsafe to create a str containing invalid UTF-8 is undefined behavior.
Note that Rust only care about UTF-8 code point validity, not grapheme cluster validity.
About nullable string comparision: In Java you can directly equals. In JS you can directly ===. But in Rust, comparing optionsl strings is not trivial:
- Comparing a
Option<String>with&str:a.as_deref() == Some(b) - Comparing a
Option<&str>withString:a == Some(b.as_str()) - Comparing a
Option<String>withOption<&str>:a.as_deref() == b
The as_deref is not intuitive. It turns Option<String> into Option<&str>. The as_str turns String into &str. Rust has deref auto conversion that can auto convert &String to &str, but that auto conversion sometimes doesn't work with generics, so some as_deref as_str is required.
Summarize the contagious things
- Borrowing that cross function boundary is contagious. Just borrowing a wheel of car indirectly borrows the whole car.
- Contagious borrow between branches. If the output of a branch indirect borrows matched value, then that borrow contaminates another branch.
- Mutate-by-recreate is contagious. Recreating child require also recreating parent that holds the new child, and parent's parent, and so on.
- Lifetime annotation is contagious. If a type has a lifetime parameter, then every type that holds it must also have lifetime parameter. Every function that use them also need lifetime parameter (except when lifetime elision works). Adding/removing lifetime parameter to a type may require changing many code.
asyncis contagious.asyncfunction can call normal function. Normal function cannot easily callasyncfunction (but it's possible to call by blocking). Many non-blocking functions tend to become async because they may call async function.- Being not
Sync/Sendis contagious. A struct that indirectly owns a non-Syncdata is notSync. A struct that indirectly owns a non-Senddata is notSend. - Error passing is contagious. If panic is not acceptable, then all functions that indirectly call a fallible function must return
Result. Related: NaN is contagious in floating point computation.
Some arguments
- "Rust doesn't ensure safety of
unsafecode. There are real vulnerabilities in Rust code: first Linux vulnerability in Rust code. So using Rust provides no value.". No. This is perfect solution fallacy. One solution being imperfect doesn't mean it's useless. If you keep the amount ofunsafesmall, you only need to inspect these small amount ofunsafecode. In C/C++ you need to inspect all related code. - "There are sanitizers in C/C++ that help me catch memory safety bugs and thread safety bugs, so Rust has no value." No. Some memory safety and thread safety bugs only trigger in production environments and in client's computers, but don't reproduce in test environment. There are Heisenbugs that can evade sanitizers. Elaborated below.
- "Using arena still face the equivalent of 'use after free', so arena doesn't solve the problem". No. Arenas can make these bugs much more deterministic than raw use-after-free bugs, preventing them from becoming Heisenbugs, making debugging much easier.
- "Rust borrow checker rejects your code because your code is wrong." No. Rust can reject valid safe code.
- "Circular reference is bad and should be avoided." No. Circular reference can be useful in many cases. Linux kernel has doubly linked lists. But circular reference do come with risks.
- "Rust guarantees high performance." No. If one evades borrow checker by using
Arc<Mutex<>>everywhere, the program will be likely slower than using a normal GC language (and has more risk of deadlocking). But it's easier to achieve high performance in Rust. In many other languages, achieving high perfomance often require bypassing (hacking) a lot of language functionalities. - "Rust guarantees security." No. Rust doesn't ensure memory/thread safety of
unsafecode 20. Also, not all security issues are memory/thread safety issues. According to Common Weakness Enumeration 2024, many real-world vulnerabilities are XSS, SQL injection, directory traversal, command injection, missing authentication, etc. that are not memory/thread safety. - "Rust makes multi-threading easy, as it prevents data race." No. Although Rust can prevent data race, it cannot prevent deadlocks. Async Rust also has traps including blocking scheduler thread and cancellation safety.
- "Rust doesn't help other than memory/thread safety." No.
- Algebraic data type (e.g.
Option,Result) helps avoid creating illegal data from the source. Using ADT data require pattern match all cases, avoiding forgetting handling one case (except when using escape hatch likeunwrap()). - Rust reduces bugs caused by unwanted accidental mutation.
- Explicit
.clone()avoids accidentally copying container like in C++. - Managing dependencies is much easier in Rust than in C/C++.
- Rust's generics, traits and standard library design learned from mistakes in C++.
- ...
- Algebraic data type (e.g.
- "Memory safety can only be achieved by Rust." No. Most GC languages are memory-safe. 21 Memory safety of existing C/C++ applications can be achieved via Fil-C.
- "Manual memory management is always faster than tracing GC." No. Moving GCs 22 have better throughput in allocation and deallocation 23 24. In manual memory management, freeing a large structure may cause big lag. Using
Arcinvolves atomic operations which may become bottleneck when contended. - "The old C/C++ codebases are already battle-tested, so there is no value in rewriting them in Rust." No. If they won't ever add any new feature and don't do any large refactoring, only accepting small bug fixes, then they would indeed become more stable and safe over time. However, if they adds new feature or do large refactoring, then new memory/thread safety issues could emerge.
- "
.unwrap()should never be used because Cloudflare outage Nov 18, 2025 is caused by.unwrap()." No. Although.unwrap()is one cause of that Cloudflare outage, there are many other causes, including: no thorough testing in test environment before deploying to production, rolling out change too quick, rollback not early enough, etc.unwrap()is sometimes useful for cases that compiler cannot prove impossible. Note that it's still recommended to reduce usages ofunwrap()in production code (can useanyhowcrate which allows convenient?on most errors 25).
The yields of paying "Rust cost"
Rust has a lot of constraints and adds frictions in coding. What are the benefits after paying this cost?
One important benefit of Rust is to prevent most Heisenbugs.
The Heisenbugs are non-deterministic. When you try to debug it, it may stop triggering. Heisenbugs are often sensitive to timing and memory layout:
- Enabling logging and enabling sanitizers makes program run slower, which may make Heisenbug no longer trigger (or become much harder to trigger).
- Breakpoint debugger also changes timing when debugging, which may make Heisenbug no longer trigger.
- Some Heisenbugs only trigger in release build, not debug build. Sometimes it's due to timing. Sometimes it's caused by optimizations related to undefined behaviors.
- Some Heisenbugs only trigger in production environment. Some Heisenbugs only happen in client's computer that developer cannot touch.
Heisenbugs are hard to debug, especially in large codebases.
Most Heisenbugs are related to memory safety, thread safety and mutation. Rust prevents most Heisenbugs compared to C/C++, so it greatly saves debugging time on Heisenbugs.
Note that there are still Heisenbugs that Rust cannot catch, including:
- Data race outside of memory (data race in disk, database, distributed system, etc.).
- Conditional deadlocks. Conditional
RefCellborrow conflict. - Async cancellation issues.
- Heisenbugs related to
unsafeand FFI (foreign function interface).
Also note that not all memory/thread safety bugs are Heisenbugs. Many are still easy to trigger and debug.
Rust is also a filter to AI. Rust constraints can catch some kinds of bugs. (Although Rust takes more tokens, because AI often need to edit multiple times to make code compile.)
Footnotes
-
The native Rust ownership relation form a tree. Reference counting (
Rc,Arc) allows shared ownership. ↩ -
Note that here "reference" here means reference in general OOP context (where there is no distinction between ownership and non-owning reference, think about reference in Java/C#/JS/Python). This is different to the Rust reference. I will use "borrow" for Rust reference in this article. ↩
-
The view type solves struct field contagious borrow but doesn't solve container contagious borrow. To encode the information of borrowing
i-th element of aVecinto type, it requires dependent type, depending on runtime value ofi. Adding dependent type into language is much more complex. ↩ -
Often the borrow checker issues (including contagious borrow issue) can be workarounded by refactoring: reorganize data structure, reorganize code and abstractions. However, new requirements can easily break existing architecture, so using refactoring to tackle borrow checker issues will require frequent large refactoring. "The most fundamental issue is that the borrow checker forces a refactor at the most inconvenient times." See also . If you don't want frequent refactoring, one solution is to use the combination of: arenas + persistent containers + deferred mutation (deferred event handling). ↩
-
Standard library has
split_offthat mutates the container. multi_mut provides a solution of split borrow ofBTreeMap. ↩ -
Exact numbers may be different. The idea is that the "performance cost contribution" of code is highly biased (fat-tail distribution). ↩
-
JetBrains IDEs semantic coloring can be configured so that captured values are in another color. This can make capturing more obvious. ↩
-
Having both ID and object reference introduces friction: translating between ID and object reference. Some ORM will malfunction if there exists two objects with the same primary key. ↩
-
Each slotmap ensures key uniqueness, but if you mix keys of different slotmaps, the different keys of different slotmap may duplicate. Using the wrong key may successfully get an element but logically wrong. id-arena avoids that by attaching arena id into key, but that makes key larger. ↩
-
Sometimes, having fine-grained lock is slower because of more lock/unlock operations. But sometimes having fine-grained lock is faster because it allows higher parallelism. Sometimes fine-grained lock can cause deadlock but coarse-grained lock won't deadlock. It depends on exact case. ↩
-
Some GC (e.g. ZGC) use load barrier. But that load barrier doesn't involve atomic read-modify-write operation so it's faster than cloning
Arc. ↩ -
See also. That was in 2020. Unsure whether it changed now. One possible reason is that ARM allows weaker memory order than X86. Also, Swift and Objective-C use reference counting almost everywhere, so possibly Apple payed more efforts in optimizing atomic reference counting. ↩
-
Tracing GC is faster for short-lived programs (such as some CLI programs and serverless functions), because there's no need to free memory for individual objects on exit. Example: My JavaScript is Faster than Your Rust. The same optimization is also achievable in Rust, but require extra work (e.g.
mem::forget, bump allocator). ↩ -
It lags because it need to do many counter decrement and deallocation for each individual object. Can be workarounded by sending the
Arcto another thread and drop in that thread. Also, for deep structures, dropping may stack overflow. ↩ -
Contended atomic operations (many threads touch one atomic value at the same time) are much slower than when not contended. Its cost also include memory block allocation and freeing. ↩
-
GC frequency is roughly porpotional to allocation speed divide by free memory. In generational GC, a minor GC only scans young generation, whose cost is roughly count of living young generation objects. But it still need to occasionally do full GC. ↩
-
When running in tools like Miri, the pointer provenance will be tracked at runtime. ↩
-
Some may intuitively think
'staticis top type (likeanyin TypeScript andObjectin Java) because it's the most "general". However, in Rust, lifetime is constraint, so the most general one is no constraint, and the most specific one is the hardest constraint. The relation is inverted. In Rust narrowing lifetime is safe but expanding lifetime is not safe, similar to java converting any type toObjectis safe but convertingObjectto another type doesn't necessarily work. ↩ -
a() || b()will not executeb()ifa()returns true.a() && b()will not executeb()ifa()returns false. ↩ -
A wrong
unsafecode in Rust can make memory/thread safety issue trigger in safe code. The impact ofunsafecode is not limited tounsafecode. ↩ -
Golang is not memory-safe under data race. Golang strings, fat pointers and slices has tearing issue. Golang map is not thread-safe. ↩
-
Golang GC is non-moving. Most other mainstream GC (e.g. Hotsopt JVM, CLR) are moving. ↩
-
In Rust, bump allocator can also achieve high throughput of allocation and deallocation. But using bump allocator requires extra work (contagious lifetime annotations). The conventional "malloc/free" allocators often has lower throughput than an optimized moving GC because they need to do more bookkeeping. Note that moving GC require much more free memory to achieve high throughput. Without enough free memory, moving GC will cause big lag. ↩
-
It's commonly told that moving GC has another benefit: handling memory fragmentation. When not using moving GC, fragmentation can still be alleviated by better allocation strategy (similar size-class allocate together). Fragmentation is also alleviated by virtual memory (memory fragmentation in page level don't waste physical memory). Also, RAM is cheaper now, so fragmentation cost is more affordable. Fragmentation is not a problem now (except for some rare cases). Moving GC can theoretically improve cache locality by avoiding fragmentation, but manual memory management can improve cache locality by reusing just-freed memory region. Fragmentation wastes memory but moving GC require larger free memory to achieve high thoughput. ↩
-
anyhowcannot auto-wrapMutexpoison error. Becauseanyhowcan only wrap errors that are standalone ('static, doesn't borrow non-global thing). Mutex poison error is not standalone. If you don't want to mutex poison to affect web server availability, can useparking_lotlocks. ↩